Best practices for teaching phonemic awareness activities include LETRS, an acronym that stands for Language Essentials for Teachers of Reading and Spelling. This approach emphasizes the importance of explicit and systematic instruction in phonemic awareness, letter recognition, and sound-symbol relationships.
By implementing these strategies, educators can lay a solid foundation for literacy development in their students.
LETRS provides a comprehensive framework for teaching phonemic awareness, with a focus on developing students’ ability to identify, isolate, and manipulate sounds in words. This includes activities such as blending and segmenting sounds, identifying rhyming words, and manipulating phonemes to create new words.
Teaching Methods: Best Practices For Teaching Phonemic Awareness Activities Include Letrs

Effective phonemic awareness instruction requires a systematic approach that includes:
Explicit Instruction
- Provide explicit instruction on phonemic awareness concepts, such as identifying and isolating sounds in words.
- Use clear and concise language to explain the concepts and provide examples.
Multisensory Activities
- Incorporate multisensory activities that engage students’ auditory, visual, and kinesthetic senses.
- Activities may include clapping rhythms, tapping sounds, or using letter tiles to build words.
Repeated Practice
- Provide repeated opportunities for students to practice phonemic awareness skills.
- Use a variety of activities and games to keep students engaged and motivated.
Feedback and Assessment
- Provide ongoing feedback to students on their progress.
- Use assessment tools to monitor students’ understanding and identify areas for improvement.
Activities and Games
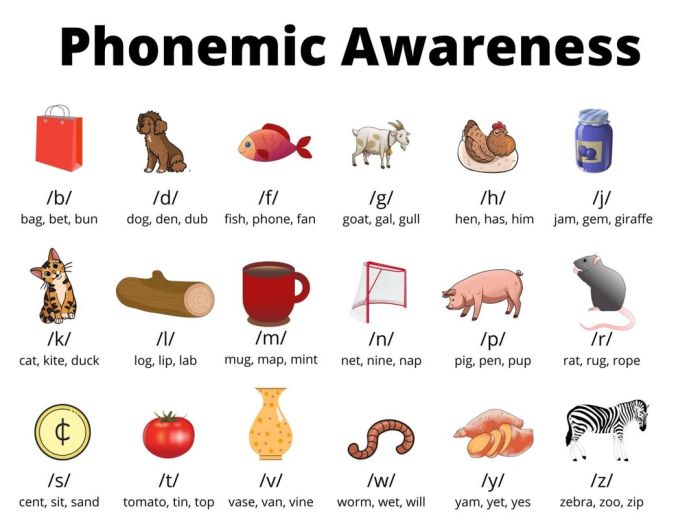
Letter Recognition
- Letter hunts: Hide letters around the room and have students find them.
- Letter matching: Provide students with sets of letters and have them match uppercase and lowercase letters.
Sound-Symbol Relationships
- Sound-letter mapping: Have students match letters to the sounds they represent.
- Sound blending: Provide students with a series of sounds and have them blend them together to form words.
Phonemic Segmentation
- Word clapping: Have students clap the sounds in words.
- Sound boxes: Provide students with boxes or squares to represent the sounds in words.
Differentiation and Assessment
Differentiation
- Provide varying levels of support and challenge based on students’ needs.
- Use scaffolding techniques, such as providing word banks or visual aids.
Assessment
- Use informal assessments, such as observations and checklists, to monitor students’ progress.
- Use formal assessments, such as phonemic awareness tests, to measure students’ overall phonemic awareness skills.
Integration with Other Literacy Skills
Reading
- Phonemic awareness supports decoding and word recognition.
- Students who have strong phonemic awareness skills are better able to sound out words and read fluently.
Writing, Best practices for teaching phonemic awareness activities include letrs
- Phonemic awareness supports spelling and word building.
- Students who have strong phonemic awareness skills are better able to segment words into sounds and spell them correctly.
Vocabulary
- Phonemic awareness supports vocabulary development.
- Students who have strong phonemic awareness skills are better able to identify and manipulate sounds in words, which helps them to learn new words.
Technology Integration

Apps and Software
- There are a variety of apps and software programs that can be used to support phonemic awareness instruction.
- These apps and programs provide interactive activities and games that make learning fun and engaging.
Online Games
- There are also a number of online games that can be used to support phonemic awareness instruction.
- These games provide a fun and interactive way for students to practice their phonemic awareness skills.
Collaboration and Partnerships
Teachers
- Teachers play a vital role in supporting phonemic awareness development.
- They can provide explicit instruction, incorporate phonemic awareness activities into their lessons, and monitor students’ progress.
Parents
- Parents can also play a role in supporting phonemic awareness development.
- They can read to their children, play phonemic awareness games, and provide opportunities for their children to practice their phonemic awareness skills.
Other Professionals
- Other professionals, such as speech-language pathologists and reading specialists, can also provide support for phonemic awareness development.
- They can work with students who have difficulty with phonemic awareness and provide specialized instruction.
Essential FAQs
What are the key components of LETRS?
LETRS focuses on five key components: phonemic awareness, letter knowledge, phonics, fluency, and vocabulary.
How can I incorporate LETRS into my phonemic awareness instruction?
There are many ways to incorporate LETRS into phonemic awareness instruction, such as using blending and segmenting activities, identifying rhyming words, and manipulating phonemes to create new words.
What are the benefits of using LETRS to teach phonemic awareness?
LETRS provides a systematic and explicit approach to teaching phonemic awareness, which can help students develop a strong understanding of the sound-symbol relationships that are essential for reading and spelling success.