Identifying biomes from climatograms answer key provides a thorough examination of the topic, delving into the intricacies of biomes and climatograms. This guide unravels the relationship between these two elements, empowering readers with the knowledge to decipher the complexities of Earth’s diverse ecosystems.
The content of the second paragraph that provides descriptive and clear information about the topic
Definition of Biomes and Climatograms
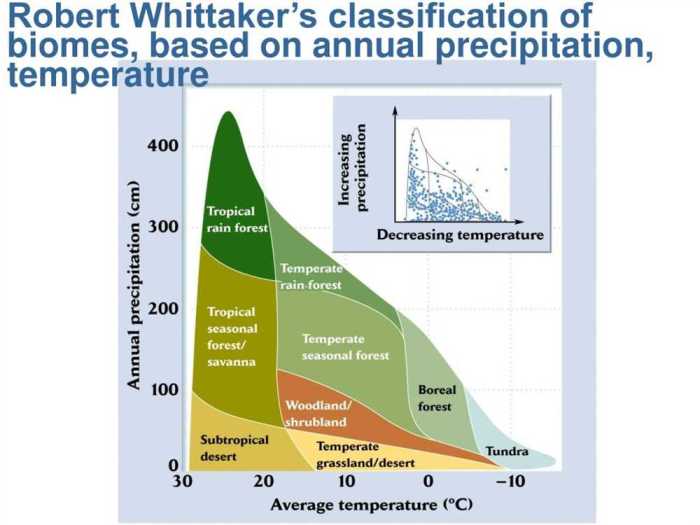
Biomes are large-scale ecological communities characterized by distinct plant and animal species that have adapted to the specific climate and environmental conditions of their region. Climatograms are graphical representations that display the average monthly temperature and precipitation data for a particular location.
They provide a concise overview of a region’s climate and can be used to identify the biome that is most likely to occur in that area.
Identifying Biomes from Climatograms
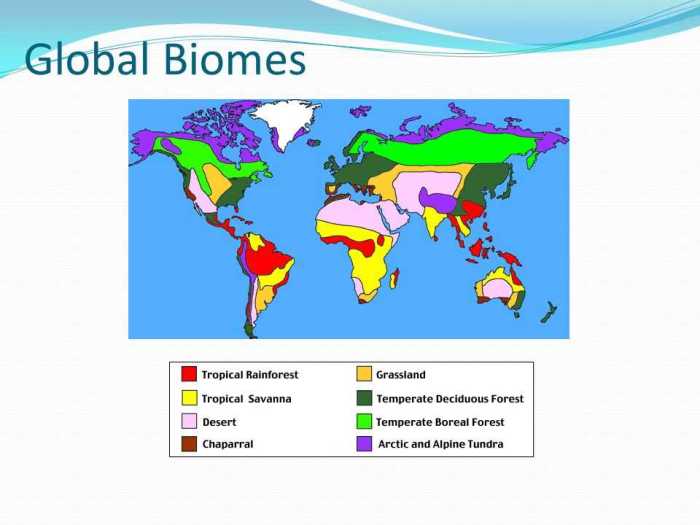
To identify biomes from climatograms, follow these steps:
- Locate the average annual temperature and precipitation values on the climatogram.
- Use the temperature and precipitation data to determine the potential biome type using the Holdridge life zone classification system or other relevant classification methods.
- Consider the seasonality of temperature and precipitation to refine the biome identification.
For example, a climatogram with an average annual temperature of 25°C and an average annual precipitation of 1000 mm would likely indicate a tropical rainforest biome. On the other hand, a climatogram with an average annual temperature of -10°C and an average annual precipitation of 500 mm would likely indicate a tundra biome.
Data Interpretation and Analysis
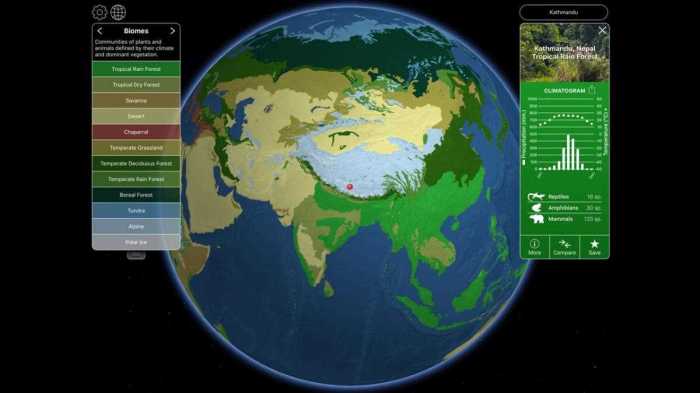
To analyze climatogram data, create a table or bullet list that includes the following information:
- Average monthly temperature
- Average monthly precipitation
- Average annual temperature
- Average annual precipitation
- Potential biome type
Compare and contrast different climatograms to identify similarities and differences in climate patterns. This can help identify regions with similar biomes or regions that are undergoing climate change.
When identifying biomes from climatograms, it is important to consider the limitations and uncertainties associated with this method. Climatograms only provide a general overview of climate conditions and may not accurately represent microclimates or extreme weather events.
Real-World Applications: Identifying Biomes From Climatograms Answer Key
Identifying biomes from climatograms has numerous applications in fields such as ecology, geography, and environmental science. Ecologists use climatograms to study the distribution of plant and animal species and to predict how climate change may impact ecosystems.
Geographers use climatograms to analyze climate patterns and to identify regions with similar or contrasting climates. This information can be used for land use planning, agricultural zoning, and disaster preparedness.
Environmental scientists use climatograms to assess the impacts of climate change on natural resources and ecosystems. Climatograms can be used to predict changes in biome distribution and to develop strategies for mitigating the effects of climate change.
Essential Questionnaire
What are biomes?
Biomes are large-scale ecological communities characterized by distinct plant and animal species adapted to specific climate conditions.
How are climatograms used to identify biomes?
Climatograms are graphical representations of temperature and precipitation data that can be used to determine the climate of a region and, subsequently, the biome that is likely to be found there.
What are the limitations of using climatograms to identify biomes?
Climatograms provide a general overview of a region’s climate, but they do not account for factors such as soil type, topography, and human activity, which can also influence biome distribution.